Area of kite is the space enclosed by a kite. A kite is a quadrilateral in which two pairs of adjacent sides are equal. The elements of a kite are its 4 angles, its 4 sides, and 2 diagonals. In this article, we will focus on the area of a kite and its formula.
| 1. | What is the Area of a Kite? |
| 2. | Area of a Kite Formula |
| 3. | Derivation of the Area of Kite Formula |
| 4. | FAQ's on Area of a Kite |
The area of a kite can be defined as the amount of space enclosed or encompassed by a kite in a two-dimensional plane. Like a square, and a rhombus, a kite does not have all four sides equal. The area of a kite is always expressed in terms of units 2 for example, in 2 , cm 2 , m 2 , etc. Let us learn about the area of a kite formula in our next section.
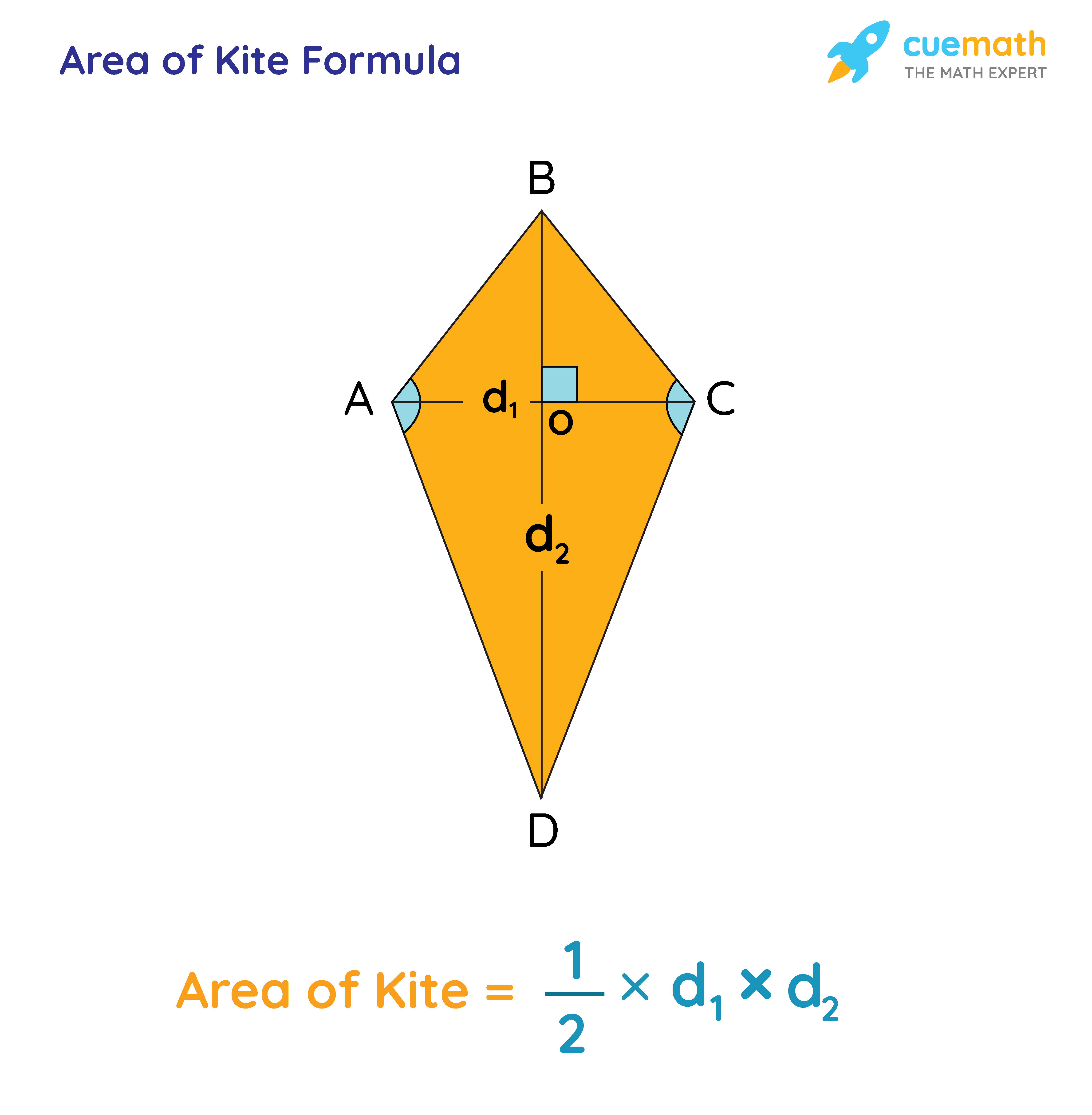
The area of a kite is half the product of the lengths of its diagonals. The formula to determine the area of a kite is: Area = ½ × (d)1 × (d)2. Here (d)1 and (d)2 are long and short diagonals of a kite.
The area of kite ABCD given below is ½ × AC × BD.

BD = Long diagonal and AC = Short diagonal
Consider a kite ABCD as shown above.
Assume the lengths of the diagonals of ABCD to be AC = p, BD = q
We know that the longer diagonal of a kite bisects the shorter diagonal at right angles, i.e., BD bisects AC and ∠AOB = 90°, ∠BOC = 90°.
AO = OC = AC/2 = p/2
Area of kite ABCD = Area of ΔABD + Area of ΔBCD. (1)
Area of a triangle = ½ × Base × Height
Now, we will calculate the areas of triangles ABD and BCD
Area of ΔABD = ½ × AO × BD = ½ × p/2 × q = (pq)/4
Area of ΔBCD = ½ × OC × BD = ½ × p/2 × q = (pq)/4
Therefore, using (1)
Area of kite ABCD = (pq)/4 + (pq)/4
= (pq)/2
Substituting the values of p and q
Area of a kite = ½ × AC × BD
Important Notes
Example 1: Four friends are flying kites of the same size in a park. The lengths of diagonals of each kite are 12 in and 15 in. Determine the sum of areas of all the four kites. Solution: Lengths of diagonals are: (d)1 =12in (d)2 =15in The area of each kite is: A = ½ × (d)1 × (d)2
= ½ × 12 × 15
= 90 in 2 Since each kite is of the same size, therefore the total area of all the four kites is 4 × 90 = 360in 2 .
Therefore the area of the four kites is 360in 2
Example 2: Kate wants to give a kite-shaped chocolate box to her friend. She wants to paste a picture of herself with her friend to cover the top of the box. Determine the area of the top of the box if the diagonals of the lid of the box are 9 in and 12 in. Solution: (d)1 = 9in (d)2 = 12in Since the box is kite-shaped, therefore the area of the top of the box is: A = ½ × (d)1 × (d)2
= ½ × 9 × 12
Therefore, the area of the top of the box is 54in 2
Example 3: Find the area of a kite if its diagonals are of the length 12 units and 5 units respectively. Solution: The area of a kite can be calculated if the length of its diagonals is known. So, Area of a kite = 1/2 × diagonal 1 × diagonal 2. After substituting the values we get, Area of a kite = 1/2 × 12 × 5 = 30 unit 2
Show Answer >
Become a problem-solving champ using logic, not rules. Learn the why behind math with our Cuemath’s certified experts.